Discover, Learn, immerse, Connect
National Library
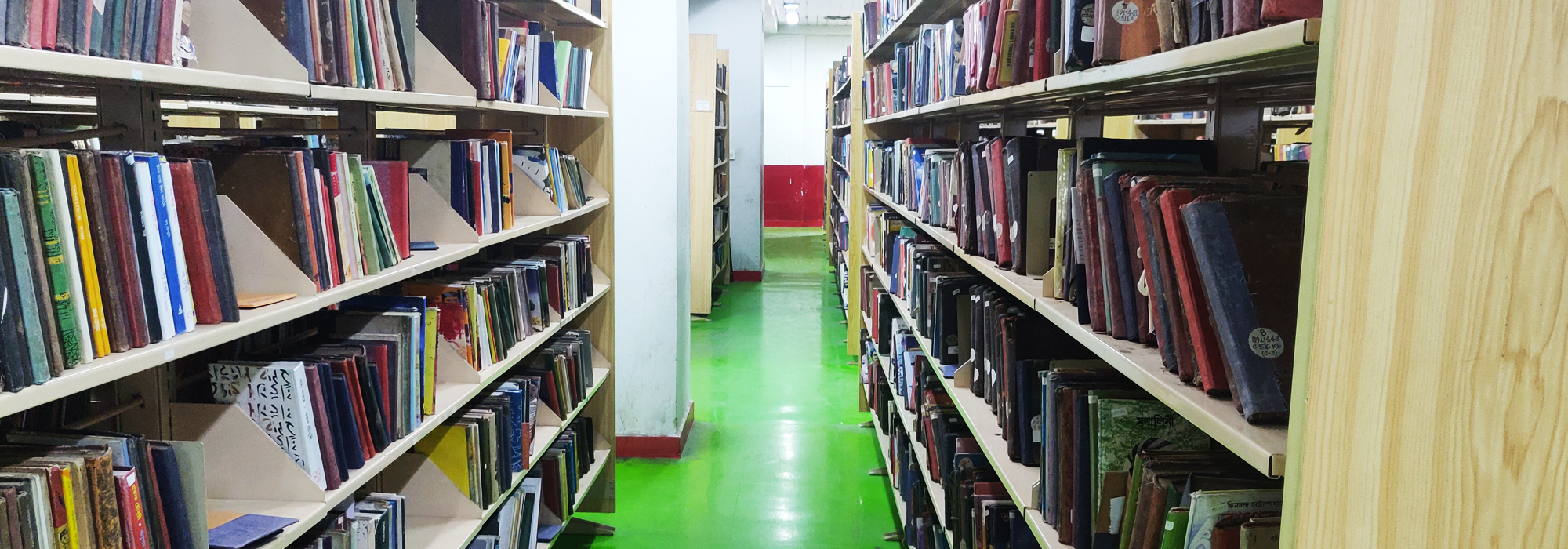
Records Available In: English, Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Malayalam, Marathi, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu, Foreign Languages: Arabic and Persian, East Asian Languages, Germanic Languages, Slavonic Langu
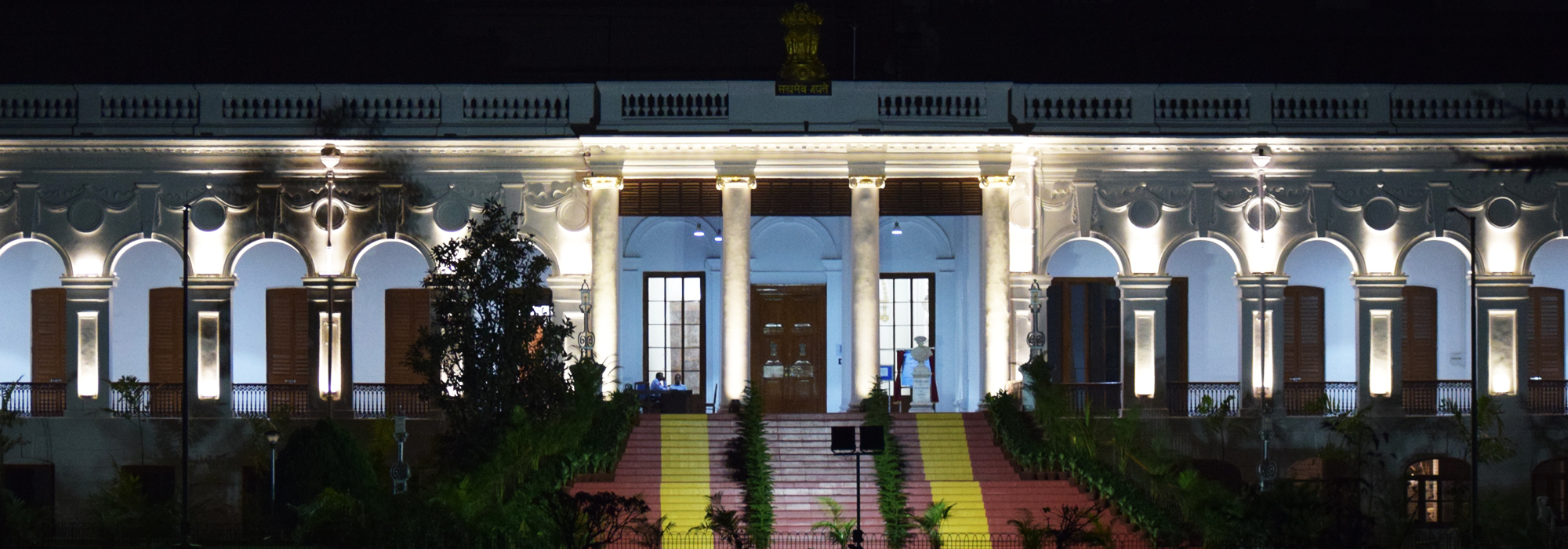
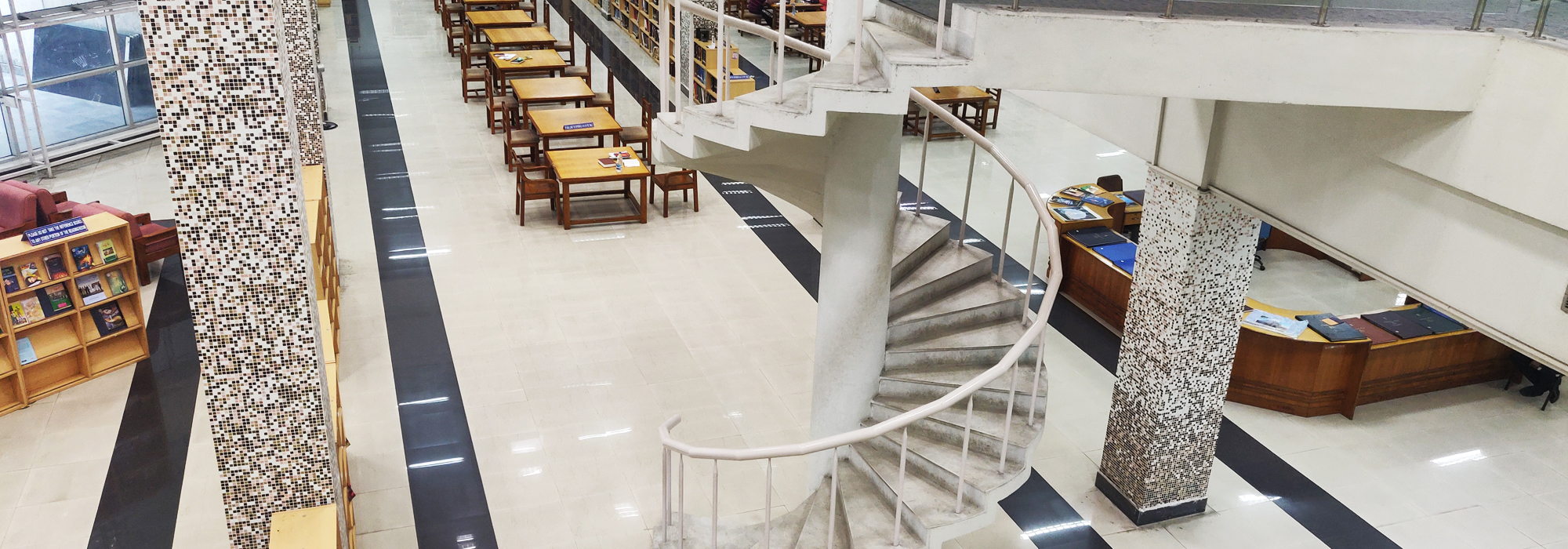
The National Library came into being in the place of the Imperial Library by the Imperial Library (Change of Name) Act in 1948. It was accorded the special status of an Institution of National Importance by Article 62 of the 7th Schedule of the Union List of the Constitution of India and Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, the then Union Minister of Education opened the library to the public on 1st February 1953. The origin of the National Library is traced to the former Calcutta Public Library. Established in the first half of the 19th century, it was opened to the public on 21st March 1836. The Calcutta Public Library was subsequently merged with the Imperial Library and combining the collection of a number of secretariat libraries, the Imperial Library was opened to the public on January 1903. The National Library, Kolkata is the National Library of India and the National Repository. It is also a legal deposit library of India, where books published in the country are deposited under Delivery of Books Act, 1954.
 Government of India
Government of India